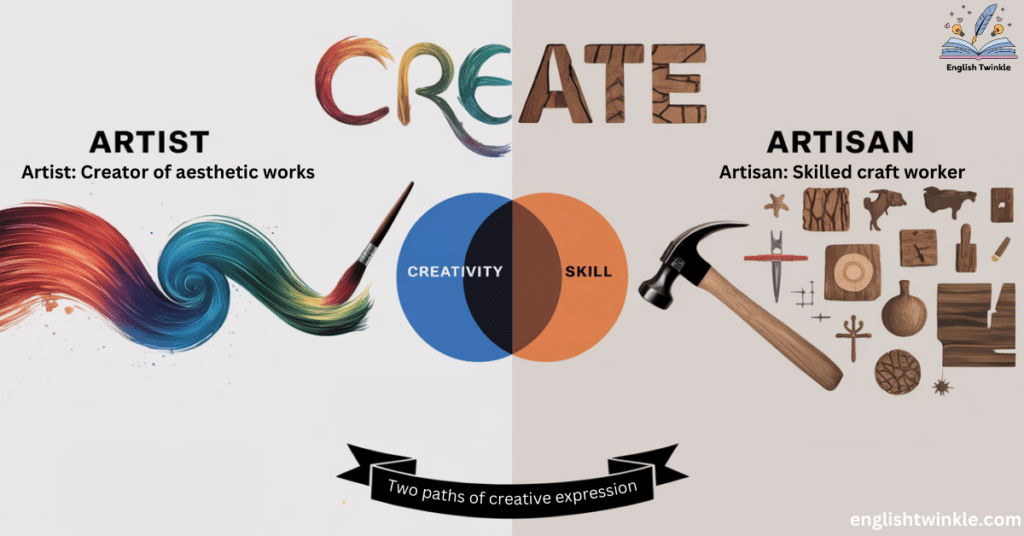
difference between artist and artisan
In the vibrant world of creativity, two terms often dance around each other, sometimes overlapping, sometimes diverging: artist and artisan. While both are masters of their craft, the distinction between these two creative forces is as nuanced as it is fascinating. This exploration will dive deep into the realms of artistic creativity and skilled craftsmanship, unraveling the threads that bind and separate these two vital contributors to our cultural landscape.
The Creative Spectrum: Where Art Meets Craft
The line between art and craftsmanship has always been blurry, a testament to the rich tapestry of human creativity. In today’s creative economy, understanding the difference between an artist and an artisan isn’t just academic—it’s crucial for appreciating the diverse forms of expression that enrich our lives.
At first glance, the distinction might seem clear: artists create, while artisans craft. But dig a little deeper, and you’ll find a world where expressive art and functional art often intersect, challenging our preconceptions about creativity and utility.
Key Terms and Their Meanings
| Term | Definition | Example | Synonyms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artist | A person who creates art as an occupation or hobby | Painter, sculptor | Creator, visionary |
| Artisan | A skilled worker who makes things by hand | Woodworker, potter | Craftsperson, maker |
| Creativity | The use of imagination or original ideas to create something | Inventing a new style of painting | Innovation, originality |
| Craftsmanship | The quality of design and work shown in something made by hand | A finely crafted wooden chair | Workmanship, artistry |
The Artist’s Realm: A Canvas of Imagination
Defining the Modern Artist
In the contemporary world, an artist is often seen as a visionary, someone who pushes boundaries and challenges perceptions. They’re the dreamers, the rebels, the ones who make us see the world through fresh eyes.
“Every artist dips his brush in his own soul, and paints his own nature into his pictures.” – Henry Ward Beecher
This quote encapsulates the essence of artistic creativity—a deeply personal journey of expression that transcends mere technique.
The Evolution of the Artist’s Role
Throughout history, the role of the artist has transformed dramatically:
- Renaissance: Artists as craftsmen and innovators
- Romantic Era: The rise of the artist as a visionary genius
- Modern Age: Artists as social commentators and provocateurs
- Digital Era: The democratization of artistic creation
Key Characteristics of an Artist’s Approach
- Emotional Expression: Artists often prioritize conveying feelings and ideas over functionality.
- Conceptual Thinking: The focus is on the message or concept behind the work.
- Innovation: Pushing boundaries and exploring new techniques is a hallmark of artistic practice.
The Artisan’s Domain: Mastery in Motion
The Modern Artisan Defined
An artisan is a skilled craftsperson who creates items that are both beautiful and functional. They are the guardians of traditional craftsmanship, blending age-old techniques with contemporary sensibilities.
Historical Significance of Artisans
Artisans have been the backbone of societies for millennia:
- Ancient Civilizations: Revered creators of everyday and ceremonial objects
- Middle Ages: Organized into influential guilds
- Industrial Revolution: Challenged by mass production
- Present Day: Experiencing a renaissance in the age of handmade and bespoke items
Hallmarks of an Artisan’s Methodology
- Skill-Based Expertise: Years of practice honing specific techniques
- Tradition and Technique: Drawing on established methods while innovating within them
- Functionality Meets Aesthetics: Creating objects that are both useful and beautiful
Artist vs Artisan: Unraveling the Differences
To truly understand the distinction between artists and artisans, let’s break down their approaches:
| Aspect | Artist | Artisan |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Self-expression, conceptual ideas | Utility, practical beauty |
| Process | Inspiration-driven, experimental | Commission-based, refined techniques |
| Uniqueness | One-of-a-kind pieces | Replicable items with individual touches |
| Materials | Diverse, often unconventional | Specialized, traditional |
| Training | Formal art education, self-taught | Apprenticeships, technical training |
Focus and Intent
Artists often create with the primary goal of self-expression or conveying a message. Their work might challenge, provoke, or inspire, but it’s not necessarily meant to serve a practical purpose. Artisans, on the other hand, craft items that blend beauty with functionality, creating practical art that enhances everyday life.
Creative Process
The artistic process is often driven by bursts of inspiration, with artists experimenting and pushing boundaries. Artisans typically work on commissions or create pieces that fit within their established repertoire, refining their techniques with each creation.
Uniqueness and Reproduction
While artists typically produce unique, one-of-a-kind pieces, artisans often create items that can be reproduced, albeit with individual variations. The value in an artist’s work often lies in its originality, while an artisan’s work is prized for its mastery of technique.
Materials and Tools
Artists might use a wide range of materials, often in unconventional ways, to achieve their vision. Artisans typically specialize in specific materials traditional to their craft, using time-honored tools and techniques.
The Grey Area: When Artists and Artisans Overlap
The modern creative landscape is filled with individuals who blur the lines between artist and artisan. These hybrid creatives, sometimes called “artrepreneurs,” combine the visionary approach of an artist with the skilled craftsmanship of an artisan.
Case Study: The Artistic Woodworker
Consider Sarah, a woodworker who creates functional furniture pieces that are also stunning sculptural works. Her dining tables serve a practical purpose but are designed with such artistic vision that they’re also considered fine art pieces. Sarah’s work exemplifies the beautiful overlap between art and craft.
Etymology and Cultural Context
Understanding the origins of the terms “artist” and “artisan” provides insight into their cultural significance:
Origins of “Artist”
- Latin Root: “Ars,” meaning skill or craft
- Evolution: Gradually came to mean a person who practices or is skilled in the fine arts
Origins of “Artisan”
- French Influence: From “artisien,” meaning a person skilled in an art or trade
- Adoption: Entered English in the 16th century, maintaining its association with skilled manual work
Real-World Examples and Profiles
To further illustrate the difference between artist and artisan, let’s look at some renowned figures in both fields:
Artists
- Frida Kahlo: Mexican painter known for her powerful self-portraits and works inspired by nature and Mexican culture
- Banksy: Anonymous street artist whose provocative works challenge social and political norms
Artisans
- Sam Maloof: Woodworker famous for his innovative furniture designs, especially his rocking chairs
- Dale Chihuly: Glassblower who has revolutionized the art of handblown glass
The Economic Landscape
The worlds of art and craft operate in distinct yet overlapping economic spheres:
Art Market
- Galleries, auctions, and high-end collectors
- Prices can reach millions for renowned artists
- Critics and curators play a significant role in valuation
Artisan Economy
- Craft fairs, boutiques, and online marketplaces like Etsy
- Prices based on materials, time, and skill level
- The maker movement has revitalized interest in handcrafted goods
Technology’s Influence
The digital age has transformed both artistic and artisanal practices:
- Digital Tools: 3D modeling software, digital painting programs
- 3D Printing: Allowing for complex designs in both art and craft
- Social Media: Providing platforms for artists and artisans to showcase and sell their work directly to audiences
The Future of Artists and Artisans
As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the landscape for both artists and artisans:
- Sustainability: Increasing focus on eco-friendly materials and processes
- Collaboration: Artists and artisans working together on innovative projects
- Virtual Reality: New frontiers for artistic expression and craft showcases
Emerging Hybrid Forms
The line between art and craft continues to blur, giving rise to new forms of creative expression:
- Digital Artisanship: Using technology to create handcrafted-style items
- Conceptual Craft: Merging traditional craft techniques with contemporary art concepts
- Functional Fine Art: Creating usable objects that are also considered high art
The Impact of Global Influences
In our interconnected world, both artists and artisans are increasingly influenced by global trends and traditions:
- Cross-Cultural Collaboration: Artists and artisans from different cultures working together
- Fusion Techniques: Blending traditional crafts from various cultures to create new forms
- Global Marketplaces: Online platforms allowing artists and artisans to reach worldwide audiences
Education and Training: Nurturing Creative Talent
The paths to becoming an artist or an artisan are as diverse as the creations they produce:
Artist Education
- Formal art schools and universities
- Self-taught through practice and experimentation
- Workshops and residencies
Artisan Training
- Apprenticeships with master craftspeople
- Vocational schools and technical programs
- Continuous learning through guilds and associations
The Role of Critics and Curators
In both the art and craft worlds, critics and curators play crucial roles:
- Art Critics: Analyze and interpret artworks, shaping public opinion and market value
- Craft Experts: Evaluate the quality and authenticity of artisanal works
- Curators: Select and arrange works for exhibitions, influencing trends and recognition
Philosophical Perspectives on Art vs Craft
The debate between art and craft has long been a subject of philosophical inquiry:
- Kantian Aesthetics: Emphasizes the “purposiveness without purpose” of fine art
- Marxist Theory: Examines the social and economic roles of artists and artisans
- Postmodern Views: Challenges the hierarchical distinction between high art and craft
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge on Artists vs Artisans
- What is the primary focus of an artist’s work? a) Functionality b) Self-expression c) Mass production d) Tradition
- Which of the following is more likely to be associated with an artisan? a) Conceptual art installations b) One-of-a-kind sculptures c) Handcrafted furniture d) Abstract expressionist paintings
- In the context of this article, what does “artrepreneur” refer to? a) A business-savvy artist b) An artisan who only sells online c) A hybrid creative who combines artistic vision with craftsmanship d) An art dealer
- Which historical period saw artists organized into influential guilds? a) Renaissance b) Middle Ages c) Industrial Revolution d) Modern Age
- What is a key characteristic of an artisan’s methodology? a) Focusing solely on self-expression b) Prioritizing conceptual ideas over technique c) Blending functionality with aesthetics d) Avoiding traditional methods
Answers:
- b) Self-expression
- c) Handcrafted furniture
- c) A hybrid creative who combines artistic vision with craftsmanship
- b) Middle Ages
- c) Blending functionality with aesthetics
Conclusion: Celebrating the Creative Spectrum
The distinction between artist and artisan is not about elevating one above the other, but about appreciating the unique contributions each makes to our cultural tapestry. Artists challenge us to see the world differently, while artisans enrich our daily lives with objects of beauty and function.
Whether you’re drawn to the conceptual realms of fine art or the tactile satisfaction of handcrafted goods, there’s no denying the value that both artists and artisans bring to society. By understanding and appreciating the nuances between these creative forces, we can more fully embrace the rich diversity of human creativity in all its forms.
As we continue to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of art and craft, let’s celebrate the visionaries who push boundaries and the skilled hands that keep traditions alive. After all, it’s in the interplay between innovation and tradition, between expression and function, that some of the most beautiful and meaningful creations emerge.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that both artists and artisans will play crucial roles in shaping our cultural landscape. The challenges of our time—from environmental concerns to rapid technological change—will undoubtedly influence their work, leading to new forms of expression and craftsmanship we can scarcely imagine today.
Whether you consider yourself an artist, an artisan, or simply an appreciator of creative works, remember that each piece of art or crafted object tells a story. It speaks of skill, passion, tradition, and innovation. By supporting and celebrating both artists and artisans, we ensure that our world remains rich in beauty, meaning, and the endless possibilities of human creativity.